Describe the Carbon Cycle in Your Own Words
Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment the amount of carbon in this system does not change. The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere pedosphere geosphere hydro - sphere and atmosphere of Earth.

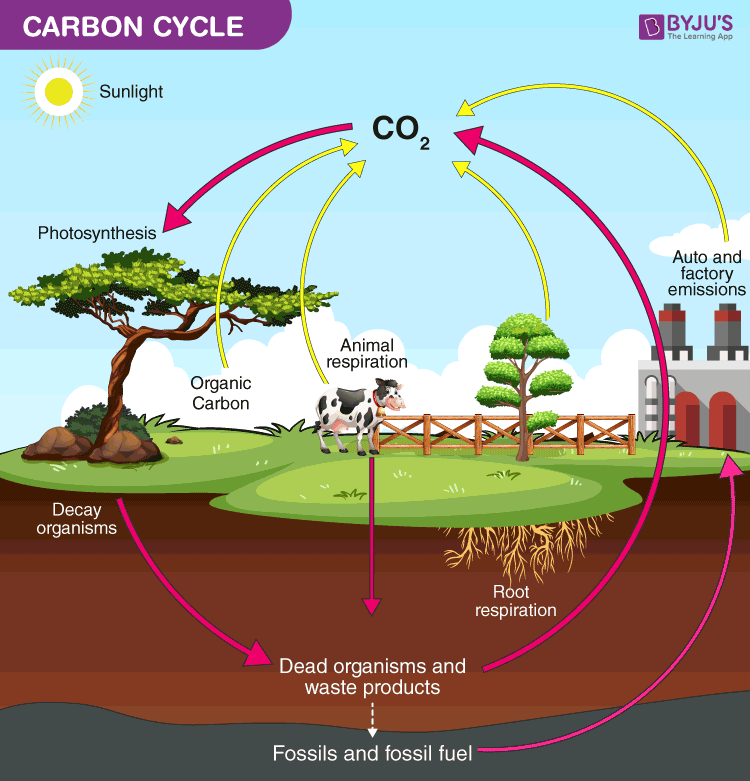
Carbon Cycle Understanding Global Change
By process of respiration and decomposition of dead organic matter it returns to the atmosphere.

. The decomposed plants and animals may then be available as fossil fuel in the. Carbon dioxide is given off when dead organisms and other organic materials decompose. The major movement of carbon.
One dealing with rapid carbon exchange among living organisms. The dead organisms dead animals and plants are eaten by decomposers in the ground. Carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth.
Up to 24 cash back The Carbon Cycle Step 4. Carbon cycle definition the circulation of carbon atoms in the biosphere as a result of photosynthetic conversion of carbon dioxide into complex organic compounds by plants which are consumed by other organisms. And c carbon gases such as CO2 carbon dioxide CH4 methane and CO carbon monoxide.
The carbon that was in their bodies is then returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Burning organic material such as fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide. Carbon Cycle is a biogeochemical cycle where various carbon compounds are interchanged among the various layers of the earth namely the biosphere geosphere pedosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere.
B organic-C such as found in organic plant material. Carbon dioxide CO 2 in the air traps heat. Carbon cycles far more slowly through geological processes such as sedimentation.
Carbon starts as Carbon ends as. They use energy from the sun to chemically combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen and oxygen from water to create sugar. Carbon storage and exchange.
Carbon cycle in biology circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. The cycle of carbon in the earths ecosystems in which carbon dioxide is fixed by photosynthetic organisms to form organic nutrients and is ultimately restored to the inorganic state as by respiration protoplasmic decay or combustion 2. For example in the food chain plants move carbon from the atmosphere into the biosphere through photosynthesis.
Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major. Carbon cycle involves a continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere and organisms. The source of the carbon found in living matter is carbon dioxide CO 2 in the air or dissolved in water.
So the carbon cycle can be described as the exchange of carbon between the land the oceans the atmosphere and the Earths interior. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. There are two types of carbon cycles that we are going to learn about.
Combustion burning Carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and uses it to make organic compounds. Carbon from the atmosphere moves to green plants by the process of photosynthesis and then to animals.
The main forms are a Inorganic-C in rocks such as bicarbonate and carbonate. There are several different forms of carbon that we have to keep track of in learning about the carbon cycle. Carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs including plants and animals which is why they are considered carbon life forms.
Algae and terrestrial green plants producers are the chief agents of carbon dioxide fixation through. Inorganic exchange is mainly between the atmosphere and hydrosphere. A cycle is a sequence of changing states that produces a final state identical to the original one.
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged between the biosphere geosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere of the Earth. One dealing with long-term cycling of carbon through geologic processes. Process in which cells use carbon dioxide water and light energy to make oxygen and glucose an energy-storing sugar.
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere pedosphere geosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere of the Earth. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere or on Earth is constantly in flux. The carbon cycle is most easily studied as two interconnected subcycles.
Although we will look at them separately its important to realize these cycles are linked. Biogeochemical cycle through which carbon is recycled through the atmosphere biosphere and geosphere. Definition of carbon cycle.
Fuel eg methane or wood Glucose. The carbon returns to the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide as a result of respiration decay by fungi bacteria etc and combustion of fossil fuels. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle.
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. In the carbon cycle carbon is constantly removed from and returned to. The carbon cycle is the system of biological and chemical processes that make carbon available to living things for use in tissue building and energy release Kinoshita 242.
The continuous movement of carbon between different living things on Earth and between living things and the environment through natural physical processes and also through the burning of fossil fuels. All life on Earth is based on carbon the sixth element of the periodic tableThe term carbon cycle refers to the movement of carbon in various forms between Earths biogeochemical reservoirs. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds many of which are essential to life on Earth.
A cycle of thermonuclear reactions in which four hydrogen atoms synthesize into a helium atom by the. Carbon moves from one storage reservoir to another through a variety of mechanisms. The oceans the atmosphere plants animals and soils on land the land biosphere and the geosphere rocks.
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again. In some circumstances the process of decomposition is prevented. The movement of carbon through the surface interior and atmosphere of the Earth.
Computer models used to track Earths natural carbon cycle have projected a slowdown in CO2 uptake by oceans and plants. Carbon exists in atmospheric gases in dissolved ions in the hydrosphere and in solids as a major component of organic matter and sedimentary rocks and is widely distributed. All living cells are composed of proteins consisting of carbon hydrogen oxygen and nitrogen in various combinations and each living organism puts these elements together according to its own.
The carbon cycle involves the exchange of carbon between living organisms biotic and their atmosphere abiotic.
Comments
Post a Comment